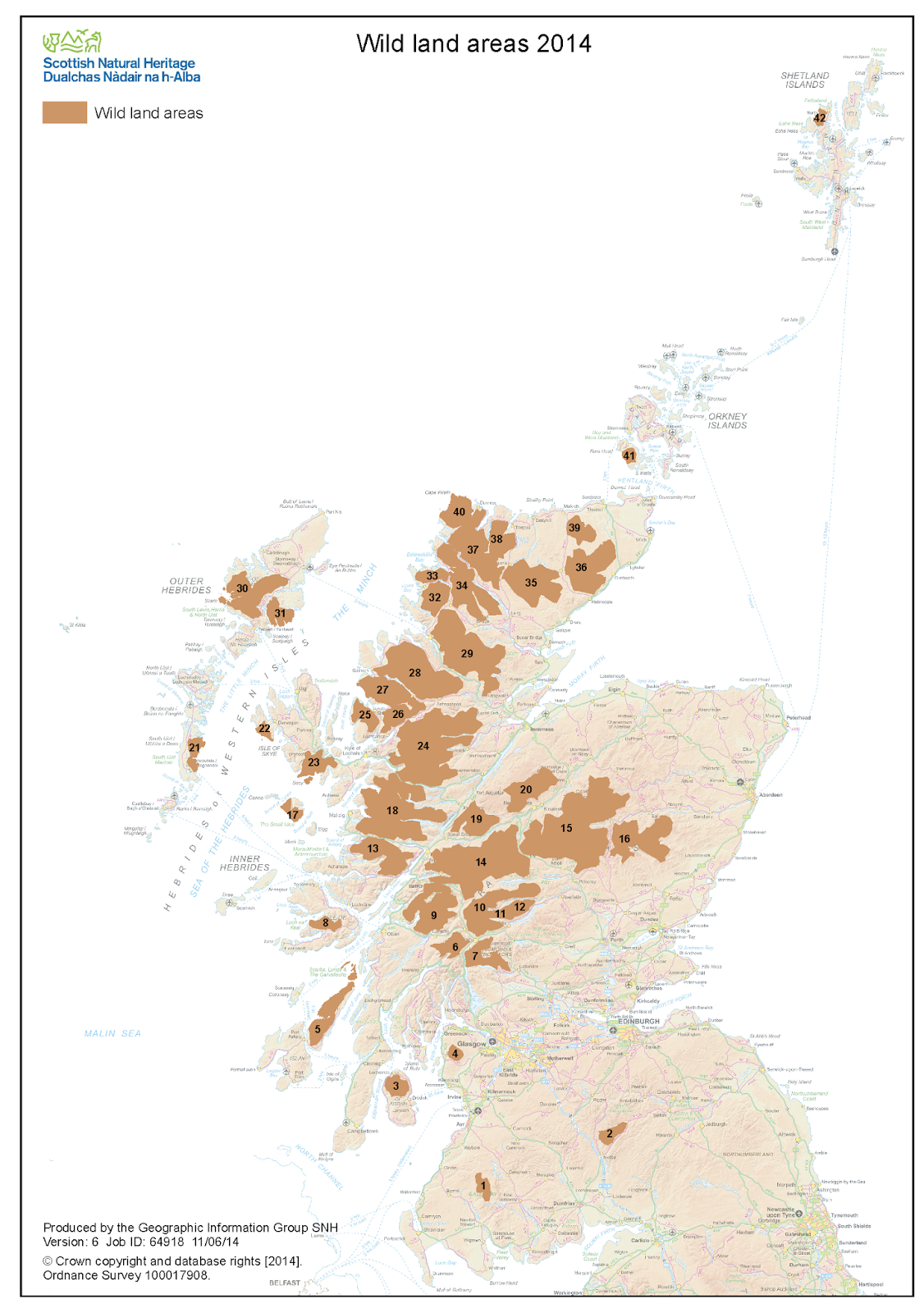
Scottish Natural Heritage has published its 2014 map of Wild Land Areas of Scotland - designated areas of coast, upland and undeveloped land - or 'wilderness' - which should be considered inviolate. Some of the areas are notably under protection via bodies such as National Parks, the John Muir Trust, or the National Trust and other private bodies, but the worrying note is that since the draft map was published in 2013, 0.8% of wild land has been developed (20.3% down to 19.5%). If it continued at that rate we'd have no wild land left by 2039 . . .
The conclusions of the report and mapping were as follows:
- The concepts of wildness and safeguarding of wild land enjoy strong support from the public and many stakeholders in Scotland. Areas of wild land are widely acknowledged as important assets, providing a number of significant ecosystem services that support a range of social and economic benefits and outcomes.
- Despite the inherent subjectivity of the concept, the physical qualities most strongly associated with wildness and identification of wild land can be mapped in a robust and repeatable way through applying a systematic and transparent methodology.
- A map of wild land areas important in the national context is required in order to provide greater clarity to all stakeholders and better inform decisions affecting them.
- The name ‘Core Areas of Wild Land’ resulted in some confusion and we therefore propose the use of the nomenclature of ‘Wild Land Areas’. We suggest that the application of this name should be restricted in use to those areas shown on the map.
- The map of wild land areas should be considered a useful and important strategic tool in decision making. Its application will be enhanced by two further pieces work that are being developed during 2014-15: descriptions of the character and nature of each of the areas, and revision of our interim guidance on assessing the effects of proposals on wild land which allows a case by case assessment of proposals in relation to wildness character.
I like the fourth point that there s no such thing as a 'core' area of wildness, it either is or isn't wild. However, there are some who may consider the issue of remoteness and wildness much more complex. For example, what about wild urban areas and brownfield sites (landlocked 'waste' land, no matter how small); underwater wildness; community (commons) wildness versus private, estate-managed (landlorded) wildness . . . it's a complex issue but it's welcome seeing SNH producing a map which can be used practically to inform major policy decisions on what we should just leave alone if we can.